Setup CI/CD for Declarative Migrations
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) became a standard requirement in modern engineering. When applied to database schemas, CI/CD ensures that changes are validated, tested, reviewed, and shipped safely across environments.
This doc introduces how to set up a CI/CD pipeline for declarative (state-based) database schema migrations with Atlas. It covers automated planning, validation and pre-approval workflows, ad-hoc approval policies, and deployment of schema changes so the final migrations are correct, predictable, and safe to apply for production.
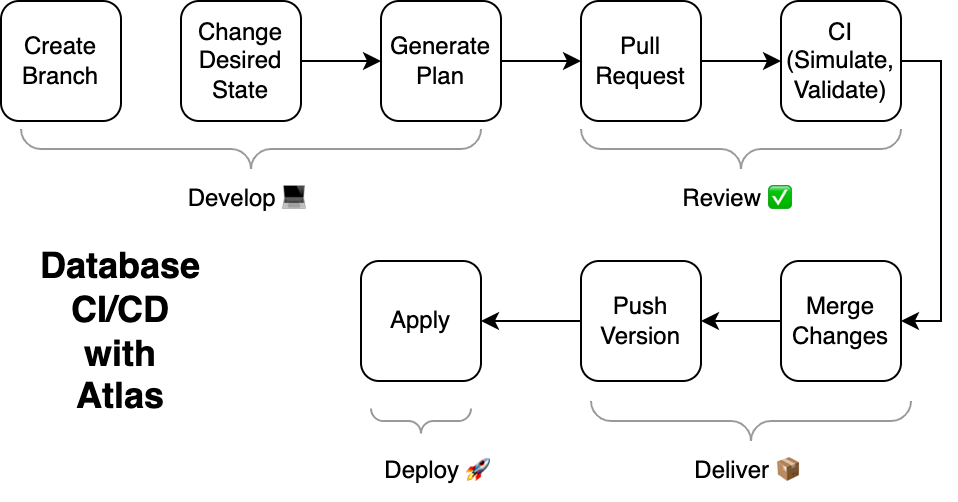
For a deeper understanding of the principles behind this workflow, see our Modern Database CI/CD blueprint.
Choose Your Workflow
Atlas supports two types of schema management workflows: declarative (state-based) migrations, and versioned migrations. This guide focuses on setting up CI/CD for declarative migrations.
Declarative (State-based) Migrations (Used in this guide)
Define the desired state of your database, and Atlas automatically calculates the migration plan. Schema changes are planned, reviewed, and approved before deployment.
Versioned Migrations
Changes are defined as explicit migration files (SQL scripts) that are applied in sequence. Each migration is tracked, version-controlled, and reviewable in pull requests.
To understand the differences and tradeoffs between these approaches, see Declarative (State-based) vs Versioned Migrations.
Prerequisites
Before setting up CI/CD, ensure you have the following:
Installing Atlas
- macOS + Linux
- Homebrew
- Docker
- Windows
- CI
- Manual Installation
To download and install the latest release of the Atlas CLI, simply run the following in your terminal:
curl -sSf https://atlasgo.sh | sh
Get the latest release with Homebrew:
brew install ariga/tap/atlas
To pull the Atlas image and run it as a Docker container:
docker pull arigaio/atlas
docker run --rm arigaio/atlas --help
If the container needs access to the host network or a local directory, use the --net=host flag and mount the desired
directory:
docker run --rm --net=host \
-v $(pwd)/migrations:/migrations \
arigaio/atlas migrate apply
--url "mysql://root:pass@:3306/test"
Download the latest release and move the atlas binary to a file location on your system PATH.
GitHub Actions
Use the setup-atlas action to install Atlas in your GitHub Actions workflow:
- uses: ariga/setup-atlas@v0
with:
cloud-token: ${{ secrets.ATLAS_CLOUD_TOKEN }}
Other CI Platforms
For other CI/CD platforms, use the installation script. See the CI/CD integrations for more details.
Atlas Pro for CI/CD
Using Atlas in CI/CD requires Atlas Pro. To activate it in your pipelines, you'll need a bot token from Atlas Cloud.
If you don't have an account yet, sign up for a free trial at auth.atlasgo.cloud or run
atlas login in your terminal.
Atlas Cloud does not access your repositories or databases. By default, Atlas Cloud only handles authentication (login) for Atlas Pro, and using the Schema Registry is optional.
The Schema Registry allows you to store, version, and maintain a single source of truth for your database schemas and migration plans. If you prefer not to use the Schema Registry, you can use an alternative storage solution accessible from your CI/CD pipeline.
Setup Your Schema Definition
If you haven't set up a declarative migrations project yet, define your desired schema before configuring CI/CD. Choose one of the following options:
 Getting Started with Schema-as-Code
Getting Started with Schema-as-Code
Define your desired schema using HCL, SQL, or through an ORM. Atlas will automatically plan and apply migrations to bring your database to the desired state.
 Import Existing Database
Import Existing Database
Import an existing database to code, then use it as your desired state. Atlas will manage schema changes going forward using declarative migrations.
CI Platform Selection
Atlas provides native integrations for all popular CI/CD platforms, with support for code comments, code suggestions, PR and run summaries, PR status updates, and more. Choose your CI platform to get started:
 GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions
Set up CI/CD pipelines using GitHub Actions with Atlas. Supports schema management with declarative migrations.
 GitLab CI
GitLab CI
Integrate Atlas with GitLab CI/CD pipelines using GitLab CI components. Full support for versioned and declarative workflows.
 CircleCI
CircleCI
Automate database migrations with CircleCI Orbs. Complete CI/CD integration for declarative workflows.
 Bitbucket Pipelines
Bitbucket Pipelines
Set up CI/CD using Bitbucket Pipes. Full support for declarative migrations and schema management.
 Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps
Use Azure DevOps Pipelines with Atlas. Supports GitHub and Azure Repos repositories with declarative migrations.
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI validates and plans schema changes before merging to the main branch, ensuring they are safe, correct, and ready for production. The workflow follows this pattern:
- Pull Request - Developer or an AI Code Assistant (such as Cursor or Claude Code) creates a PR with schema changes
- Schema Plan - Atlas generates a migration plan by comparing the current database state with the desired schema
- Linting and Policy Checks - Atlas checks schema changes for safety, compliance, and policy violations
- Review - Team reviews the migration plan along with the linting report posted as a PR comment
- Merge - Changes are merged to main branch
- Approve Plan - The migration plan is approved and stored in the Schema Registry
- Push Schema - The desired schema state is pushed to the Schema Registry
Schema Planning
Atlas generates migration plans by comparing your desired schema state (defined in HCL, SQL, or ORM) against the current database state.
The atlas schema plan command creates a migration plan that shows exactly what SQL statements will be executed to bring the database
to the desired state.
Atlas automatically posts plan results as comments on your pull/merge requests, providing immediate feedback to developers. For example:
- GitHub Actions
- BitBucket
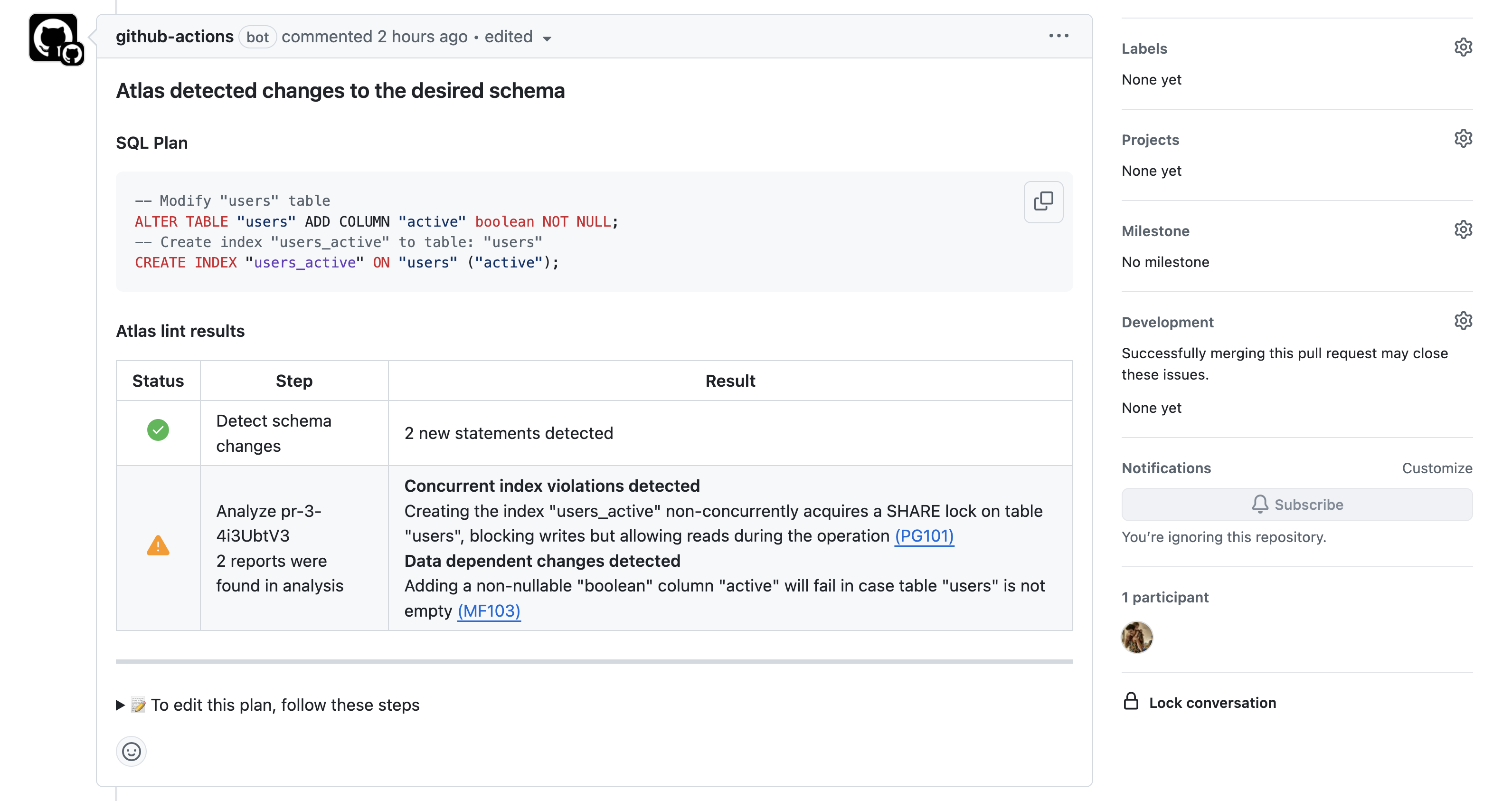

The schema-plan functionality is available to all CI platforms:
- GitHub Actions:
ariga/atlas-action/schema/plan@v1 - GitLab CI:
schema-plancomponent - Bitbucket:
schema/planpipe - Azure DevOps:
schema planaction - CircleCI:
schema_planorb
To learn more about schema planning, see the Pre-planning Schema Migrations guide.
Pre-approval Workflows
Pre-approval workflows ensure that all schema changes are reviewed and approved before being applied to production. This workflow combines schema planning during development with automatic approval on merge:
- During PR: The
schema/planaction generates a migration plan and posts it to the PR - On Merge: The
schema/plan/approveaction automatically approves the plan and stores it in the Schema Registry - On Deploy: The
schema/applyaction uses the pre-approved plan without requiring manual intervention
This creates a seamless workflow where schema changes are reviewed during development and automatically approved when merged, ensuring only reviewed changes can be deployed.
Ad-hoc Approval
While pre-approval workflows catch most schema changes during development, some scenarios require additional safety checks:
- Manual changes made directly to the database
- Schema drift detected during deployment
- Deploying to environments without CI pipelines
Ad-hoc approval acts as a final checkpoint. When atlas schema apply runs, it performs an additional check to detect any differences
between the desired schema and the actual database state. If differences are found and no pre-approved plan exists, Atlas can pause
and require manual approval before applying changes.
You can configure ad-hoc approval behavior using the lint.review policy. The policy can be set to one of the following values:
| Policy | Description |
|---|---|
ALWAYS (default) | Always require manual approval before applying schema changes. This is the safest option and ensures every change is reviewed. |
WARNING | Require approval if any diagnostics (warnings or errors) are found. This balances safety with automation by only requiring review when potential issues are detected. |
ERROR | Require approval only if severe diagnostics (errors) are found. This is the most permissive option, allowing safe changes to proceed automatically while still catching critical issues. |
Configure the policy in your atlas.hcl file:
- Global Configuration
- Per-Env Configuration
lint {
review = ERROR // ERROR | WARNING | ALWAYS
destructive {
error = false
}
}
env "prod" {
lint {
review = ALWAYS // Require approval for all changes in production
}
}
When ad-hoc approval is required, Atlas pauses the deployment and provides a link to review and approve the migration plan. Here's how it looks in different platforms:
- GitHub Actions
- Kubernetes Operator
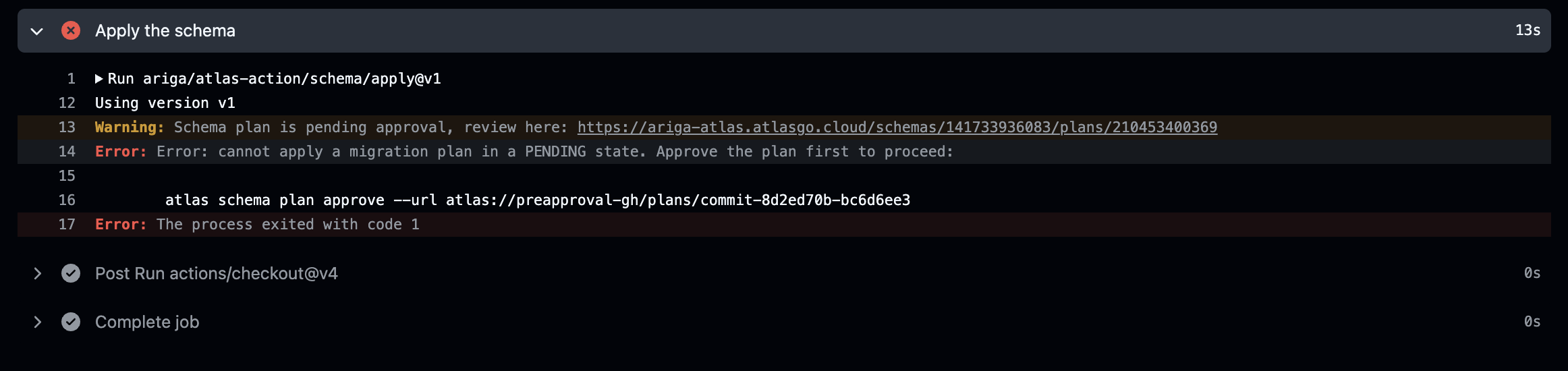
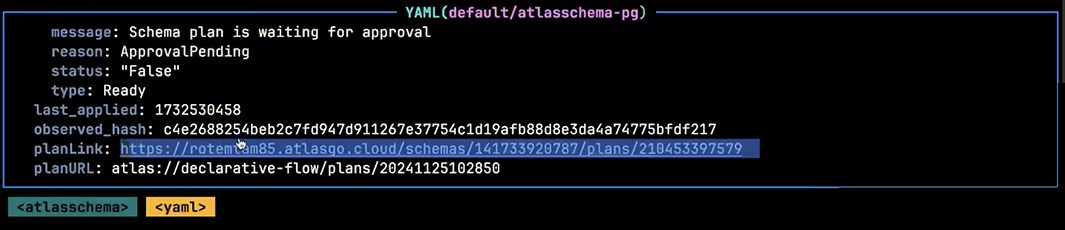
When approval is required, Atlas provides a link to the migration plan in the Atlas Registry. Clicking the link opens the plan in the registry UI where you can review the proposed changes and approve or reject them:
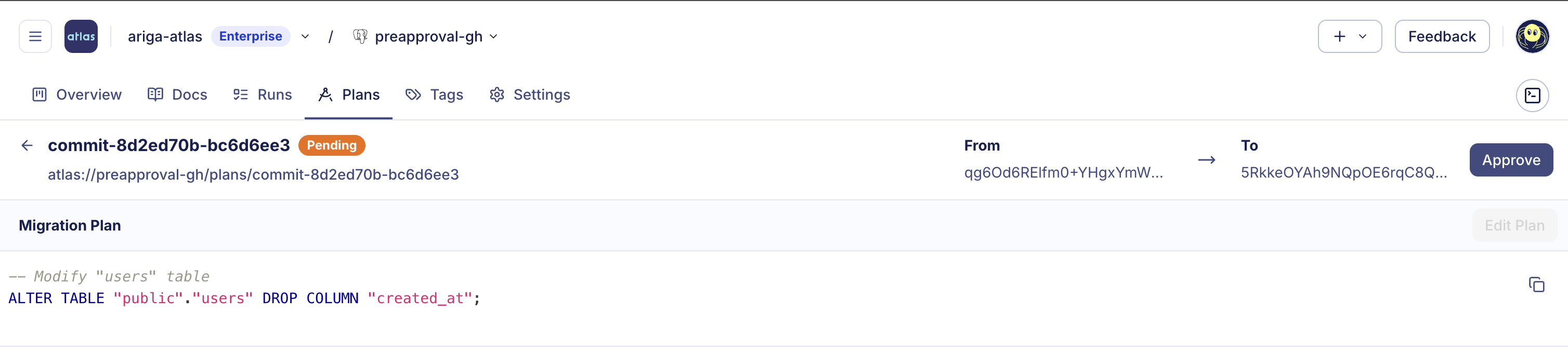
Ad-hoc approval is available on:
- GitHub Actions: Ad-hoc approval with GitHub Actions
- Kubernetes Operator: Ad-hoc approval with Kubernetes Operator (includes video guide)
Schema Push to Registry
When a pull request is merged into the main branch, Atlas lets you push your schema definition to the Atlas Schema Registry. This creates an immutable, versioned artifact (like pushing a Docker image to a container registry) that becomes the single source of truth for your schema.
The registry stores the exact schema state that passed review and planning, ensuring only approved schemas can be deployed.
Once in the registry, schemas can be deployed to any environment without needing access to your source code repository, using
URLs like atlas://myapp?tag=latest.
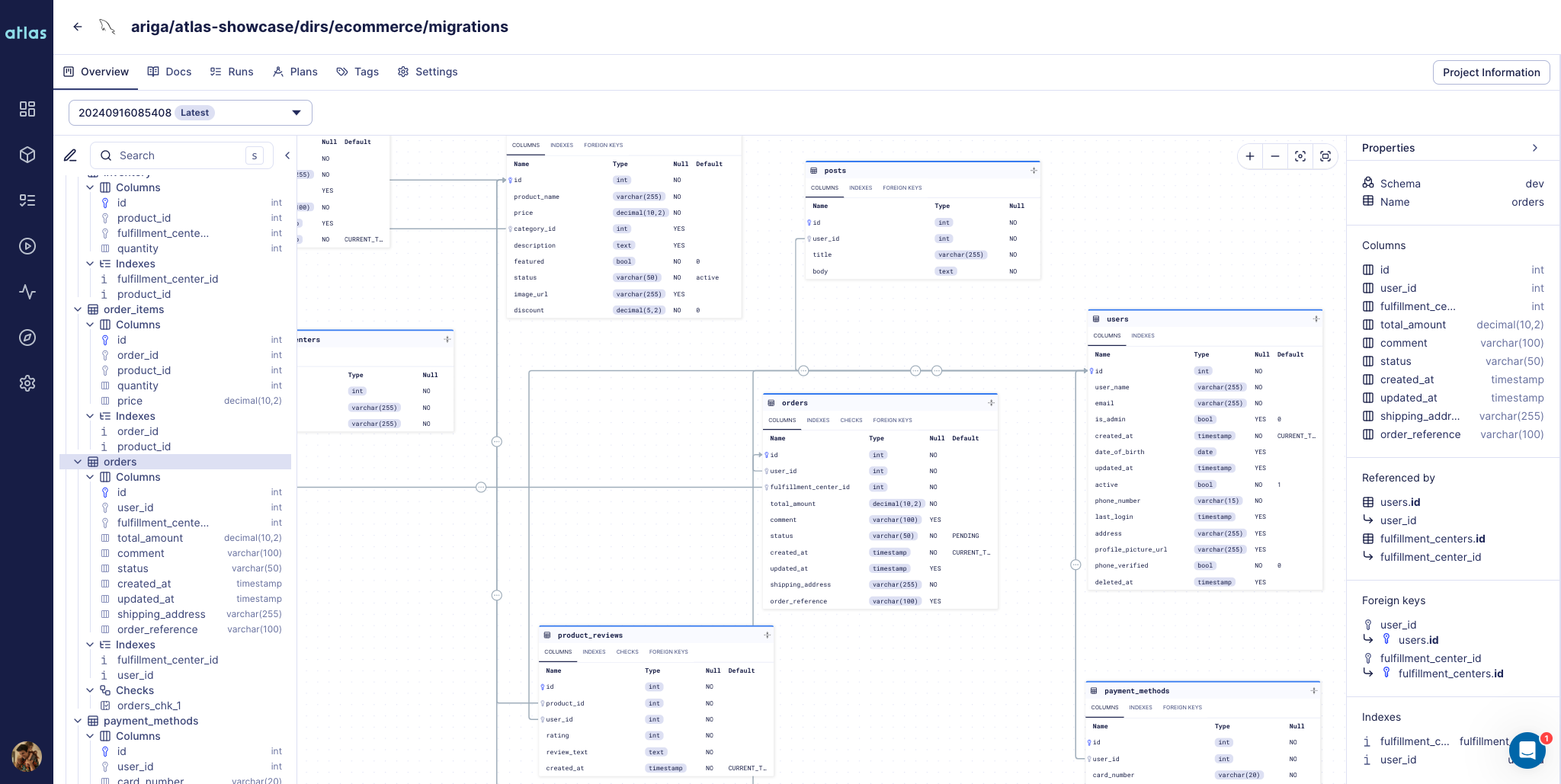
Schema created with atlas schema push
The schema-push functionality is available on most CI platforms:
- GitHub Actions:
ariga/atlas-action/schema/push@v1 - GitLab CI:
schema-pushcomponent - Azure DevOps:
schema pushtask - CircleCI: Use
atlas schema pushcommand directly withatlas-orb/setup - Bitbucket:
schema/pushpipe
Continuous Deployment (CD)
Once your schema is validated and pushed to the registry, you can deploy it to your environments. Choose the deployment method based on your infrastructure needs:
 GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions
Deploy schemas directly from your CI/CD pipeline. Simple and straightforward deployment for any environment.
 Kubernetes Operator
Kubernetes Operator
Native Kubernetes resource management using the Atlas Operator. Deploy schemas as Kubernetes resources with declarative workflows.
 Terraform
Terraform
Infrastructure as Code deployment using the Atlas Terraform Provider. Manage schemas alongside your infrastructure.
 ArgoCD
ArgoCD
GitOps deployment for Kubernetes using ArgoCD. Deploy schemas declaratively with full GitOps workflow.
 Flux CD
Flux CD
GitOps deployment alternative for Kubernetes. Continuous delivery with Git-based configuration.
 Other Options
Other Options
Additional deployment methods including ECS Fargate, Helm, and more. Find the right solution for your infrastructure.
Next Steps
Enhance your CI/CD pipeline with advanced features, such as environment promotion workflows with compliance support, real-time schema monitoring and drift detection, custom policy rules, and webhook notifications:
 Environment Promotion
Environment Promotion
Implement progressive deployments across Dev, Staging, and Production with environment segregation and compliance support for SOC 2, ISO 27002, and more.
 Schema Monitoring & Drift Detection
Schema Monitoring & Drift Detection
Get live visibility of your database schema with automated ER diagrams, changelogs, and real-time monitoring. Automatically detect when your schema drifts from its intended state and get instant alerts via Slack or webhooks.
 Custom Policy Rules
Custom Policy Rules
Define custom linting rules to enforce team practices, naming conventions, and compliance requirements. Write rules in HCL to automate policy enforcement.
 Webhooks & Notifications
Webhooks & Notifications
Set up webhooks to receive notifications about schema changes, drift detection, and deployment events in Slack or custom HTTP endpoints.
Need Help?
Have questions about setting up CI/CD with Atlas? Join our Discord community or book a demo to see Atlas in action.