Inspecting Existing Database Schemas
Atlas provides a command-line tool to inspect existing database schemas and generate their Atlas HCL definitions. With automatic schema inspection, simply provide a connection string to the target database and Atlas will print out its schema definition.
This allows users to see the current state of their schema and save it as the source of truth, enabling them to manage their schema as code with Atlas.
By default, running atlas schema inspect inspects only schemas, tables, and their associated indexes and
constraints such as foreign keys and checks.
Views, materialized views, functions, procedures, triggers, sequences, domains, extensions, and additional database features are available to Atlas Pro users. To include these resources in the inspection, use the following command:
atlas login
Flags
When using schema inspect to inspect an existing database, users may supply multiple parameters:
--urlor-u(required) - URL of the database to be inspected--schema- Schemas to inspect within the target database--exclude- Filter out resources matching the given glob pattern--include(Pro) - Include resources matching the given glob pattern--format- Specify your preferred format for the output (e.g., HCL, SQL, JSON)--webor-w(Pro) - Visualize the schema as an ERD on Atlas Cloud (see an example here)--export(Pro) - Export the schema using configured exporters
Inspect a Database
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- SQLite
- SQL Server
- ClickHouse
- Redshift
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database"
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://postgres:pass@localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://user:pass@localhost:3306"
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://localhost"
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://user:pass@localhost:3306"
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlite://file.db"
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlite://file?cache=shared&mode=memory"
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://localhost:1433?database=master&mode=database"
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://user:pass@localhost:1433?database=master&mode=database"
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://localhost:9000"
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://user:pass@localhost:9000?secure=true"
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://redshift-cluster:5439/database"
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://user:pass@redshift-cluster:5439/database?sslmode=disable"
Inspect a Single Schema
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- SQL Server
- ClickHouse
- Redshift
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database?search_path=public"
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://postgres:pass@localhost:5432/database?search_path=public&sslmode=disable"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost/schema"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://user:pass@localhost:3306/schema"
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://localhost/schema"
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://user:pass@localhost:3306/schema"
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://localhost:1433?database=master"
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://user:pass@localhost:1433?database=master"
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://localhost:9000/database"
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://user:pass@localhost:9000/database?secure=true"
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://redshift-cluster:5439/database?search_path=public"
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://user:pass@redshift-cluster:5439/database?search_path=public&sslmode=disable"
Write the Output to a File
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- SQLite
- SQL Server
- ClickHouse
- Redshift
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://postgres:pass@localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable" > schema.pg.hcl
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://user:pass@localhost:3306" > schema.my.hcl
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://user:pass@localhost:3306" > schema.ma.hcl
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlite://file.db" > schema.lt.hcl
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://user:pass@localhost:1433?database=master&mode=database" > schema.ms.hcl
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://user:pass@localhost:9000?secure=true" > schema.ch.hcl
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://user:pass@redshift-cluster:5439/database?sslmode=disable" > schema.rs.hcl
Inspect Multiple Schemas
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
- SQL Server
- ClickHouse
- Redshift
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --schema schema1 --schema schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://user:pass@localhost:3306" -s schema1,schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://localhost" --schema schema1 --schema schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "maria://user:pass@localhost:3306" -s schema1,schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable" --schema schema1 --schema schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://postgres:pass@localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable" -s schema1,schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://localhost:1433?database=master&mode=database" --schema schema1 --schema schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://user:pass@localhost:1433?database=master&mode=database" -s schema1,schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://localhost:9000/database" --schema schema1 --schema schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://user:pass@localhost:9000/database?secure=true" -s schema1,schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://user:pass@redshift-cluster:5439/database" --schema schema1 --schema schema2
atlas schema inspect -u "redshift://user:pass@redshift-cluster:5439/database?search_path=public&sslmode=disable" -s schema1,schema2
Exclude Schemas
Exclude schemas that match a glob pattern from the inspection:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "internal"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "schema_*"
Exclude Database Objects
Exclude database objects that match a glob pattern from the inspection:
# Skip extensions management.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost" --exclude "*[type=extension]"
# Exclude extension versions only.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost" --exclude "*[type=extension].version"
Exclude Schema Resources
Exclude schema resources (objects) that match a glob pattern from the inspection:
- Database Scope
- Schema Scope
When inspecting a database (multiple schemas), the first glob pattern matches the schema name, and the second matches the object name:
# Exclude all policies and functions from the public schema.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database" --exclude 'public.*[type=policy|function]'
# Exclude all policies and functions that match the pattern from all schemas.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database" --exclude '*.*[type=policy|function]'
When inspecting a specific schema, the first glob pattern matches the object name:
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database?search_path=public" --exclude '*[type=policy|function]'
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost:3306/database" --exclude '*[type=policy|function]'
Exclude Tables
Exclude tables that match a glob pattern from the inspection:
- Database Scope
- Schema Scope
When inspecting a database (multiple schemas), the first glob pattern matches the schema name, and the second matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*.prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "schema.table"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "schema.t*[type=table]" --exclude "schema.e*[type=enum]"
When inspecting a specific schema, the first glob pattern matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "table"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "t*[type=table]" --exclude "e*[type=enum]"
By default, the type=table selector excludes all table types, including base tables, partitions, and foreign tables.
If you want to exclude a specific type of table, such as partition or foreign_table, you can use more fine-grained
selectors like type=partition or type=foreign_table. For example:
# Database scope excluding all partitions.
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*.*[type=partition]"
# Schema scope excluding all foreign tables.
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*[type=foreign_table]"
Exclude Table Resources
Exclude columns, indexes, or foreign-keys that match a glob pattern from the inspection:
- Database Scope
- Schema Scope
When inspecting a database (multiple schemas), the first glob pattern matches the schema name, and the second matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*.*.prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "public.*.c1"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "public.*.c*[type=column|index]"
When inspecting a specific schema, the first glob pattern matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*.prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*.c1"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --exclude "*.c*[type=column|index]"
Include Schemas Atlas Pro
Include only schemas that match a glob pattern during inspection:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "internal"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "schema_*"
Include Schema Resources Atlas Pro
Include only schema resources (objects) that match a glob pattern from the inspection:
- Database Scope
- Schema Scope
When inspecting a database (multiple schemas), the first glob pattern matches the schema name, and the second matches the object name:
# Include only the policies and functions from the public schema.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database" --include 'public.*[type=policy|function]'
# Include only policies and functions matching the pattern from all schemas.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database" --include '*.*[type=policy|function]'
When inspecting a specific schema, the glob pattern matches the object name:
# Include only the policies and functions from the schema.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database?search_path=public" --include '*[type=policy|function]'
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost:3306/database" --include '*[type=policy|function]'
Include Tables Only Atlas Pro
Include only tables that match a glob pattern from the inspection. All other resources will be excluded:
- Database Scope
- Schema Scope
When inspecting a database (multiple schemas), the first glob pattern matches the schema name, and the second matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "*.prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "schema.table"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "schema.t*[type=table]" --include "schema.e*[type=enum]"
When inspecting a specific schema, the first glob pattern matches the table name:
# Include only tables from the schema.
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://localhost:5432/database?search_path=public" --include '*[type=table]'
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost:3306/database" --include '*[type=table]'
Include Table Resources (Table Triggers Only) Atlas Pro
Include only triggers that match a glob pattern from the inspection. All other resources will be excluded:
- Database Scope
- Schema Scope
When inspecting a database (multiple schemas), the first glob pattern matches the schema name, and the second matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "*.*.prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "public.*.tg"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "public.*.c*[type=trigger]"
When inspecting a specific schema, the first glob pattern matches the table name:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "*.prefix_*"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "*.tg"
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --include "*.c*[type=trigger]"
SQL Format
By default, the output of schema inspect is in the Atlas DDL. However, you can use SQL to describe the desired schema
in all commands that are supported by Atlas DDL. To output the schema in SQL format, use the --format flag as follows:
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://localhost" --format "{{ sql . }}"
JSON Format
Atlas can output a JSON document that represents the database schema. This representation allows users to use tools
like jq to analyze the schema programmatically.
atlas schema inspect -u '<url>' --format '{{ json . }}'
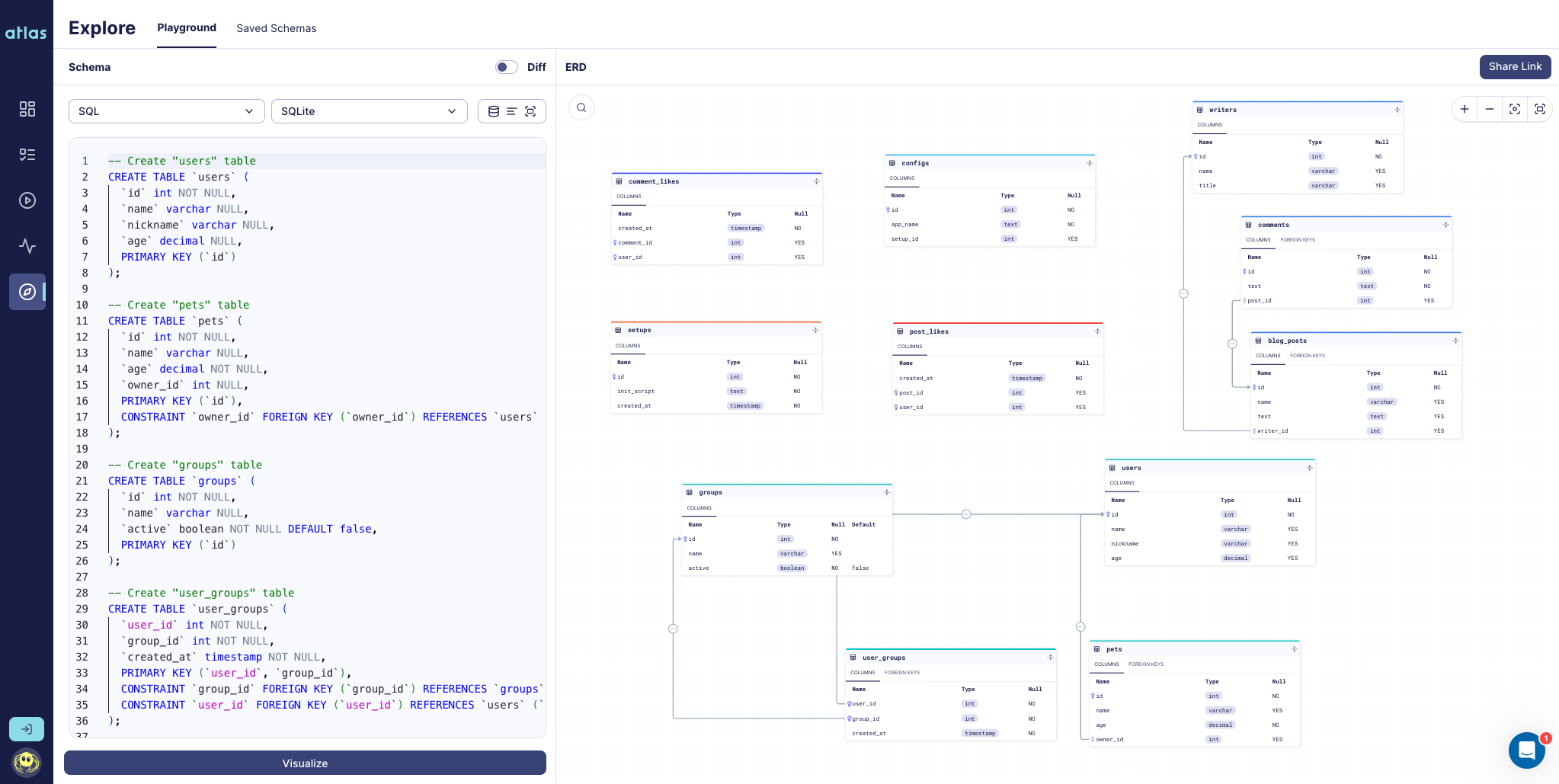
Visualize Schemas
Atlas can generate an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) for the inspected schemas. The following command shows how to generate an ERD for inspected schemas:
atlas schema inspect -u '<url>' -w
Export Schema Using Exporters Atlas Pro
The --export flag is available exclusively to Pro users. To use this feature, run:
atlas login
The --export flag exports the inspected schema using pre-configured exporters defined in your atlas.hcl.
This allows for automated, repeatable exports to files or external services.
atlas schema inspect --env prod --export
Exporters are configured in your project file and referenced in the environment's export block:
- SQL
- HCL
- HTTP
- Multiple Exporters
exporter "sql" "schema" {
path = "schema"
split_by = object
}
env "prod" {
url = "postgres://localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable"
export {
schema {
inspect = exporter.sql.schema
}
}
}
exporter "hcl" "schema" {
path = "schema"
split_by = object
ext = ".pg.hcl"
}
env "prod" {
url = "postgres://localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable"
export {
schema {
inspect = exporter.hcl.schema
}
}
}
exporter "http" "webhook" {
url = "https://api.example.com/schemas"
method = "POST"
body_template = "{{ sql . }}"
headers = {
"Content-Type" = "text/plain"
}
}
env "prod" {
url = "postgres://localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable"
export {
schema {
inspect = exporter.http.webhook
}
}
}
exporter "hcl" "hcl_schema" {
path = "schema/hcl"
split_by = object
}
exporter "sql" "sql_schema" {
path = "schema/sql"
split_by = object
}
exporter "multi" "all" {
exporters = [
exporter.hcl.hcl_schema,
exporter.sql.sql_schema,
]
}
env "prod" {
url = "postgres://localhost:5432/database?sslmode=disable"
export {
schema {
inspect = exporter.multi.all
}
}
}
For the full exporter configuration reference, see the Exporters documentation.