Liquibase Diff Alternative in Atlas
Liquibase provides diff and diff-changelog commands to compare database schemas and generate changelogs from differences,
respectively. While useful, these commands have limitations: they require two live database connections, produce verbose output,
and don't integrate well with modern CI/CD workflows.
Atlas provides powerful alternatives with atlas schema diff and atlas schema inspect that offer more flexibility, better
output formats, and seamless integration with GitOps workflows.
Atlas can compare any schema sources: databases, SQL files, HCL files, ORM models, and migration directories can all be diffed against each other. In addition, Atlas produces the migration file needed to migrate the database to the desired state in standard, native SQL format.
Quick Comparison
| Capability | Atlas schema diff/inspect | Liquibase diff/diff-changelog |
|---|---|---|
| Compare any source to any | ✅ DB, SQL, HCL, ORM, migrations | ⚠️ Databases and offline snapshots only |
| Compare to schema files | ✅ SQL and HCL files directly | ❌ Not supported |
| Compare to ORM models | ✅ GORM, Ent, Django, Sequelize, etc. | ❌ Not supported |
| Output formats | ✅ SQL, HCL, JSON, ERD, custom | ✅ XML/YAML/JSON/SQL changelog |
| Visual ERD diff | ✅ Interactive ERD with diff view | ❌ Not supported |
| Drift detection | ✅ Continuous monitoring | ⚠️ Manual |
| CI/CD integration | ✅ GitHub Actions, GitLab, K8s, Argo CD, Terraform | ⚠️ CLI and plugins only |
This document is maintained by the Atlas team. It may contain outdated information or mistakes. For Liquibase's latest details, please refer to the official Liquibase website.
Comparing Database Schemas with Atlas
Atlas's schema diff command accepts any combination of schema sources for --from and --to. All sources can be compared
to each other in any combination.
 Database URLs
Database URLs
Connect directly to MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, ClickHouse, SQLite, and more using standard connection URLs.
 SQL Schema Code
SQL Schema Code
Define your schema as plain SQL DDL statements. Great for teams familiar with SQL who want version-controlled schemas.
 HCL Schema Code
HCL Schema Code
Use Atlas's declarative HCL language for type-safe schema definitions with IDE support and validation.
 Migration Directories
Migration Directories
Compare against existing migration directories to detect drift or generate new migrations from schema changes.
 ORM Models
ORM Models
Load schemas directly from your ORM: GORM, Ent, Django, SQLAlchemy, Sequelize, TypeORM, Hibernate, and more.
Compare Two Databases
Here are some examples comparing two database schemas across different database engines:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- SQL Server
- ClickHouse
- SQLite
- Redshift
- Databricks
atlas schema diff \
--from "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/prod" \
--to "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/staging"
atlas schema diff \
--from "postgres://user:pass@localhost:5432/prod?sslmode=disable" \
--to "postgres://user:pass@localhost:5432/staging?sslmode=disable"
atlas schema diff \
--from "sqlserver://sa:pass@localhost:1433?database=prod" \
--to "sqlserver://sa:pass@localhost:1433?database=staging"
atlas schema diff \
--from "clickhouse://default:pass@localhost:9000/prod" \
--to "clickhouse://default:pass@localhost:9000/staging"
atlas schema diff \
--from "sqlite://prod.db" \
--to "sqlite://staging.db"
atlas schema diff \
--from "redshift://user:pass@cluster.region.redshift.amazonaws.com:5439/prod" \
--to "redshift://user:pass@cluster.region.redshift.amazonaws.com:5439/staging"
atlas schema diff \
--from "databricks://token:dapi...@workspace.cloud.databricks.com:443/prod" \
--to "databricks://token:dapi...@workspace.cloud.databricks.com:443/staging"
Atlas outputs the SQL statements needed to transform the from schema into the to schema:
-- Add new column
ALTER TABLE "users" ADD COLUMN "phone" varchar(50);
-- Create new index
CREATE INDEX "idx_users_email" ON "users" ("email");
Compare Database to Schema Code
Unlike Liquibase, Atlas can compare a live database directly to a schema file - no reference database needed:
# Compare database to SQL schema file
atlas schema diff \
--from "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/prod" \
--to "file://schema.sql" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
# Compare database to HCL schema file
atlas schema diff \
--from "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/prod" \
--to "file://schema.hcl" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
--dev-urlThe --dev-url flag specifies a temporary database connection used by Atlas to normalize and compare schemas. This can be a
local Docker container or any development database instance. Atlas uses this connection internally and doesn't modify your
source or target schemas. Read more at: Dev Database.
Compare Any Source to Any Other
Atlas can compare any schema sources to any other. Here are some examples:
# Compare database to ORM models
atlas schema diff \
--from "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/prod" \
--to "ent://ent/schema" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
# Compare SQL file to HCL file
atlas schema diff \
--from "file://old-schema.sql" \
--to "file://new-schema.hcl" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
# Compare migration directory to database
atlas schema diff \
--from "file://migrations" \
--to "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/prod" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
# Compare two migration directories
atlas schema diff \
--from "file://migrations-v1" \
--to "file://migrations-v2" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
Inspecting and Snapshotting Schemas
Similar to Liquibase's snapshot command, Atlas can capture database schema states for any supported source, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQL Server, SQLite, ClickHouse, Redshift, Snowflake, and more.
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- SQL Server
- ClickHouse
- SQLite
- Databricks
atlas schema inspect -u "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/mydb" --format '{{ sql . }}'
atlas schema inspect -u "postgres://user:pass@localhost:5432/mydb?sslmode=disable" --format '{{ sql . }}'
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlserver://sa:pass@localhost:1433?database=mydb" --format '{{ sql . }}'
atlas schema inspect -u "clickhouse://default:pass@localhost:9000/mydb" --format '{{ sql . }}'
atlas schema inspect -u "sqlite://mydb.db" --format '{{ sql . }}'
atlas schema inspect -u "databricks://token:dapi...@workspace.cloud.databricks.com:443/mydb" --format '{{ sql . }}'
Output Formats
Atlas supports multiple output formats for schema inspection:
| Format | Command | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| SQL | --format '{{ sql . }}' | Version control, migrations |
| HCL | (default) | Atlas schema-as-code |
| JSON | --format '{{ json . }}' | Programmatic processing |
| ERD | --web | Visual documentation |
Visualize with ERD
Atlas can generate interactive Entity Relationship Diagrams when you use the --web flag:
atlas schema inspect -u "<DATABASE_URL>" --web
This opens an interactive ERD in Atlas Cloud where you can explore tables, relationships, and schema documentation.
Visual Schema Diff
Atlas can also display schema differences as a visual ERD diff, making it easy to see exactly what changed:
atlas schema diff \
--from "mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/prod" \
--to "file://schema.sql" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev" \
--web
This opens an interactive view showing added, modified, and removed tables/columns highlighted in the ERD.
Drift Detection
While Liquibase requires manually running diff-changelog to detect drift, Atlas provides both CLI-based checks and continuous
automated monitoring.
CLI Drift Check
# Check if production matches expected schema
atlas schema diff \
--from "mysql://root:pass@prod:3306/app" \
--to "file://schema.sql" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
This check can also run automatically in CI with native integrations for GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, Bitbucket Pipelines, and Azure DevOps.
Automated Drift Detection using Atlas Schema Monitoring
Atlas Schema Monitoring provides continuous, automated drift detection. It continuously compares your database schema with the expected state in real-time with minimal performance impact. You can compare database-to-database or database-to-deployment to catch drift from any source.
When drift is detected, Atlas provides instant alerts via Slack notifications or webhook integrations. You get visual ERD diffs showing exactly what drifted, along with HCL and SQL representations of the differences. Atlas also generates an SQL plan to migrate either the code or the database to the desired state, making remediation straightforward. A complete audit trail tracks all detected drifts over time.
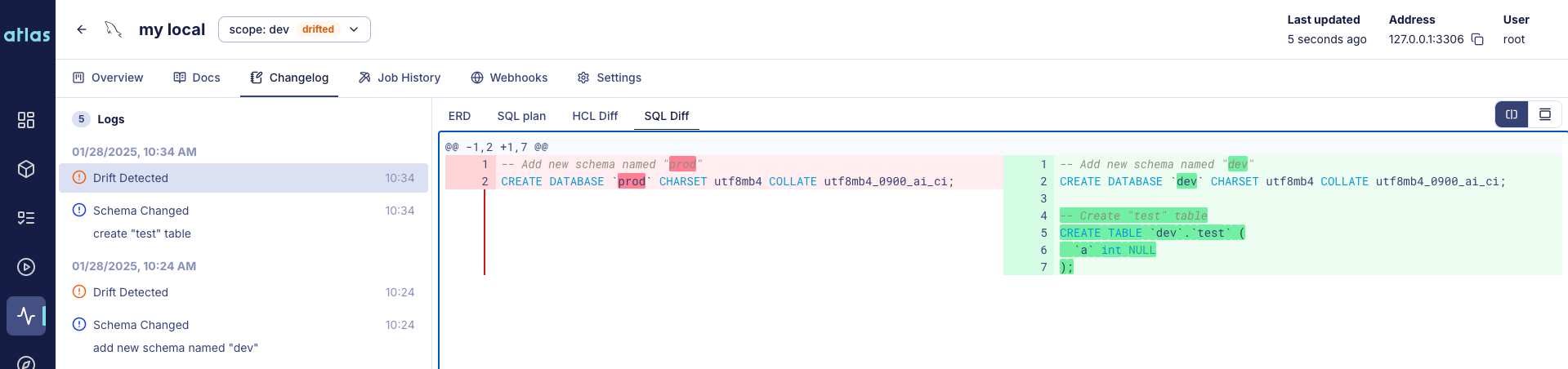
Schema Monitoring Features
Beyond drift detection, Atlas Schema Monitoring provides:
- Live schema visibility with auto-generated ER diagrams and documentation for every monitored database
- Schema statistics including table sizes, row counts, and index usage to track database growth over time
- Schema changelog tracking all changes over time, making it easy to triage schema-related issues
- Flexible deployment via both agent-less (GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Bitbucket Pipelines) and agent-based (Atlas Agent with Helm or Terraform) setups
- Webhook integrations for custom alerting and automation workflows
See Schema Monitoring for the full feature set and Drift Detection for setup instructions.
Generating Migrations
Unlike Liquibase's diff-changelog which generates changelog files, Atlas automatically generates clean SQL migration scripts
using the atlas migrate diff command. You define the desired state and Atlas computes the exact SQL needed to get there.
Automatic Migration Planning
Atlas can generate migrations from any schema source. Instead of manually writing migration scripts, you define the desired state and Atlas computes the exact SQL needed to transition your database:
- From SQL Schema
- From HCL Schema
- From Database
- From ORM
atlas migrate diff <migration_name> \
--dir "file://migrations" \
--to "file://schema.sql" \
--dev-url "docker://postgres/16/dev"
atlas migrate diff <migration_name> \
--dir "file://migrations" \
--to "file://schema.hcl" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
atlas migrate diff <migration_name> \
--dir "file://migrations" \
--to "mysql://user:pass@localhost:3306/source_db" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/dev"
Atlas can load schemas directly from your ORM models and generate migrations automatically:
atlas migrate diff <migration_name> \
--dir "file://migrations" \
--to "<orm_url>" \
--dev-url "docker://postgres/16/dev"
Supported ORMs include:
- Go: GORM, Ent, Beego, Bun
- Python: SQLAlchemy, Django
- Node.js: Sequelize, TypeORM, Prisma, Drizzle
- Other: Hibernate, Doctrine, EF Core
See ORM Integrations for setup instructions.
This creates a versioned migration file with the exact SQL statements:
CREATE TABLE "users" (
"id" bigint NOT NULL,
"name" varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
See Versioned Migrations for the complete workflow including linting and applying migrations.
Summary
Atlas provides modern, flexible alternatives to Liquibase's diff and diff-changelog commands. Unlike Liquibase which requires two database connections and produces changelog files, Atlas can compare any schema source to any other databases, SQL files, HCL files, ORM models, and migration directories — all interchangeably.
Key capabilities include:
-
Schema Comparison (
atlas schema diff) - Compare any two schema sources and produce a detailed diff. Supports multiple output formats including SQL migrations, HCL schema files, JSON for programmatic processing, and interactive ERD visualizations with the--webflag. -
Schema Inspection (
atlas schema inspect) - Capture the current state of any database and export it to version-controlled schema files in SQL or HCL format. This enables treating your database schema as code, with full support for Git workflows and code review. -
Automatic Migration Generation (
atlas migrate diff) - Generate versioned SQL migration files automatically by comparing your desired schema (from code, ORM, or HCL) against your migration directory. Atlas computes the exact SQL statements needed to reach the target state. -
Continuous Schema Monitoring - Detect schema drift in real-time with Atlas Cloud's monitoring capabilities. Get instant alerts when production schemas diverge from expected states, view visual diffs between environments, and generate SQL plans to remediate drift.
-
Native CI/CD Integration - Built-in support for GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, Bitbucket Pipelines, Azure DevOps, Kubernetes Operators, Argo CD, and Terraform. Automate schema comparisons, drift detection, and migration deployment as part of your existing workflows.