CI/CD for Databases with Azure DevOps and GitHub
Many teams use GitHub for source control but prefer Azure DevOps Pipelines for CI/CD. Azure Pipelines can seamlessly trigger from GitHub repositories, giving you the best of both platforms.
This guide walks you through setting up Atlas's automated database schema migrations with code hosted on GitHub and pipelines running on Azure DevOps.
Prerequisites
Installing Atlas
- macOS + Linux
- Homebrew
- Docker
- Windows
- CI
- Manual Installation
To download and install the latest release of the Atlas CLI, simply run the following in your terminal:
curl -sSf https://atlasgo.sh | sh
Get the latest release with Homebrew:
brew install ariga/tap/atlas
To pull the Atlas image and run it as a Docker container:
docker pull arigaio/atlas
docker run --rm arigaio/atlas --help
If the container needs access to the host network or a local directory, use the --net=host flag and mount the desired
directory:
docker run --rm --net=host \
-v $(pwd)/migrations:/migrations \
arigaio/atlas migrate apply
--url "mysql://root:pass@:3306/test"
Download the latest release and move the atlas binary to a file location on your system PATH.
GitHub Actions
Use the setup-atlas action to install Atlas in your GitHub Actions workflow:
- uses: ariga/setup-atlas@v0
with:
cloud-token: ${{ secrets.ATLAS_CLOUD_TOKEN }}
Other CI Platforms
For other CI/CD platforms, use the installation script. See the CI/CD integrations for more details.
After installing Atlas locally, log in to your organization by running the following command:
atlas login
Setting up Azure DevOps
- Create an Azure DevOps organization if you don't have one already.
- Create a new project in your Azure DevOps organization.
- Add the Atlas extension to your organization from the Azure DevOps Marketplace.
Connecting GitHub to Azure DevOps
To trigger Azure DevOps pipelines from GitHub repositories, you need to create a service connection:
- In your Azure DevOps project, go to Project Settings → Service connections.
- Click New service connection and select GitHub.
- Choose OAuth or Personal Access Token authentication method.
- If using Personal Access Token, create a GitHub personal access token with
reposcope. - Name your service connection (e.g., "GitHub Connection").
The GitHub service connection allows the AtlasAction task to post migration lint results directly as comments on your GitHub
pull requests. This provides immediate feedback to developers without requiring them to navigate to Azure DevOps to view the
results. Make sure to use the exact name of your service connection in the githubConnection parameter below.
Creating an Atlas Cloud bot token
To report CI run results to Atlas Cloud, create an Atlas Cloud bot token by following these instructions. Copy the token and store it as a secret using the following steps.
Creating secrets in Azure DevOps
In your Azure DevOps project, go to Pipelines → Library:
- Create a variable group named "atlas-vars".
- Add the following variables:
ATLAS_TOKEN- Your Atlas Cloud bot token (mark as secret)DB_URL- Your database connection string (mark as secret)
Choose a workflow
Atlas supports two types of schema management workflows:
- Versioned Migrations - Changes to the schema are defined as migrations (SQL scripts) and applied in sequence to reach the desired state.
- Declarative Migrations - The desired state of the database is defined as code, and Atlas calculates the migration plan to apply it.
This guide focuses on the Versioned Migrations workflow. To learn more about the differences and tradeoffs between these approaches, see the Declarative vs Versioned article.
Versioned Migrations Workflow
In the versioned workflow, changes to the schema are represented by a migration directory in your codebase. Each file in this directory represents a transition to a new version of the schema.
Based on our blueprint for Modern CI/CD for Databases, our pipeline will:
- Lint new migration files whenever a pull request is opened.
- Push the migration directory to the Schema Registry when changes are merged to the main branch.
- Apply new migrations to our database.
Pushing a migration directory to Atlas Cloud
Running the following command from the parent directory of your migration directory creates a "migration directory" repo in your Atlas Cloud organization (substitute "app" with the name you want to give the new Atlas repository before running):
atlas migrate push app \
--dev-url "docker://postgres/16/dev?search_path=public"
Replace docker://postgres/16/dev with the appropriate dev database URL for your database.
For more information on the dev database, see the dev database article.
Atlas will print a URL leading to your migrations on Atlas Cloud. You can visit this URL to view your migrations.
Setting up GitHub
Create an azure-pipelines.yml file in the root of your GitHub repository with the following content. Remember to replace
"app" with the real name of your Atlas Cloud repository.
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
paths:
include:
- 'migrations/*'
- 'azure-pipelines.yml'
pr:
branches:
include:
- main
paths:
include:
- 'migrations/*'
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
variables:
- group: atlas-vars
steps:
- checkout: self
persistCredentials: true
fetchDepth: 0
fetchTags: true
- script: |
echo "Configuring git user for commits..."
git config user.email "azure-pipelines[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git config user.name "azure-pipelines[bot]"
displayName: 'Configure Git User for Commits'
- script: curl -sSf https://atlasgo.sh | sh
displayName: Install Atlas
- script: atlas version
displayName: Atlas Version
- script: atlas login --token $(ATLAS_TOKEN)
displayName: Atlas Login
# Lint migrations on pull requests
- task: AtlasAction@1
condition: eq(variables['Build.Reason'], 'PullRequest')
inputs:
action: 'migrate lint'
dir: 'file://migrations'
dir_name: 'app'
config: 'file://atlas.hcl'
env: 'ci'
githubConnection: 'GitHub Connection'
displayName: Lint Migrations
# Push migrations to Atlas Cloud on main branch
- task: AtlasAction@1
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main'))
inputs:
action: 'migrate push'
dir: 'file://migrations'
dir_name: 'app'
latest: true
env: 'ci'
displayName: Push Migrations
# Apply migrations to database on main branch
- task: AtlasAction@1
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main'))
inputs:
action: 'migrate apply'
dir: 'file://migrations'
url: $(DB_URL)
displayName: Apply Migrations
Also, create an atlas.hcl file in the root of your GitHub repository with the following content:
env {
name = atlas.env
dev = "docker://postgres/16/dev?search_path=public" # Replace if necessary (see "Dev Database" above)
migration {
repo {
name = "app" # Replace with the name of your repository in previous step
}
}
}
Creating the pipeline in Azure DevOps
- In your Azure DevOps project, go to Pipelines → Pipelines.
- Click New pipeline.
- Select GitHub as your source.
- Authenticate and select your GitHub repository.
- Choose Existing Azure Pipelines YAML file.
- Select the
azure-pipelines.ymlfile you created. - Click Save and run.
Let's break down what this pipeline does:
-
Lint on Pull Requests: The
migrate lintstep runs automatically whenever a pull request is opened that modifies themigrations/directory. Atlas analyzes the new migrations for potential issues like destructive changes, backward incompatibility, or syntax errors. Because we configured thegithubConnectionparameter, lint results appear as a comment directly on the GitHub pull request. -
Push to Registry: When changes are merged into the main branch, the
migrate pushstep pushes the migration directory to Atlas Cloud's Schema Registry. This creates a versioned snapshot of your migrations that can be referenced and deployed across environments. -
Apply to Database: The
migrate applystep deploys pending migrations to your database using the connection string stored in theDB_URLsecret.
Testing the workflow
Let's take our new pipeline for a spin. Assume we have an existing migration file in our repository:
CREATE TABLE t1
(
c1 serial NOT NULL,
c2 integer NOT NULL,
c3 integer NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT pk PRIMARY KEY (c1)
);
Now let's add a new migration:
- Create a new branch in your GitHub repository and add a new migration locally
with
atlas migrate new drop_c3 --edit. Paste the following in the editor:
ALTER TABLE "t1" DROP COLUMN "c3";
-
Commit and push the changes to GitHub.
-
Open a pull request in GitHub. This will trigger the Azure DevOps pipeline and run the
migrate lintstep.
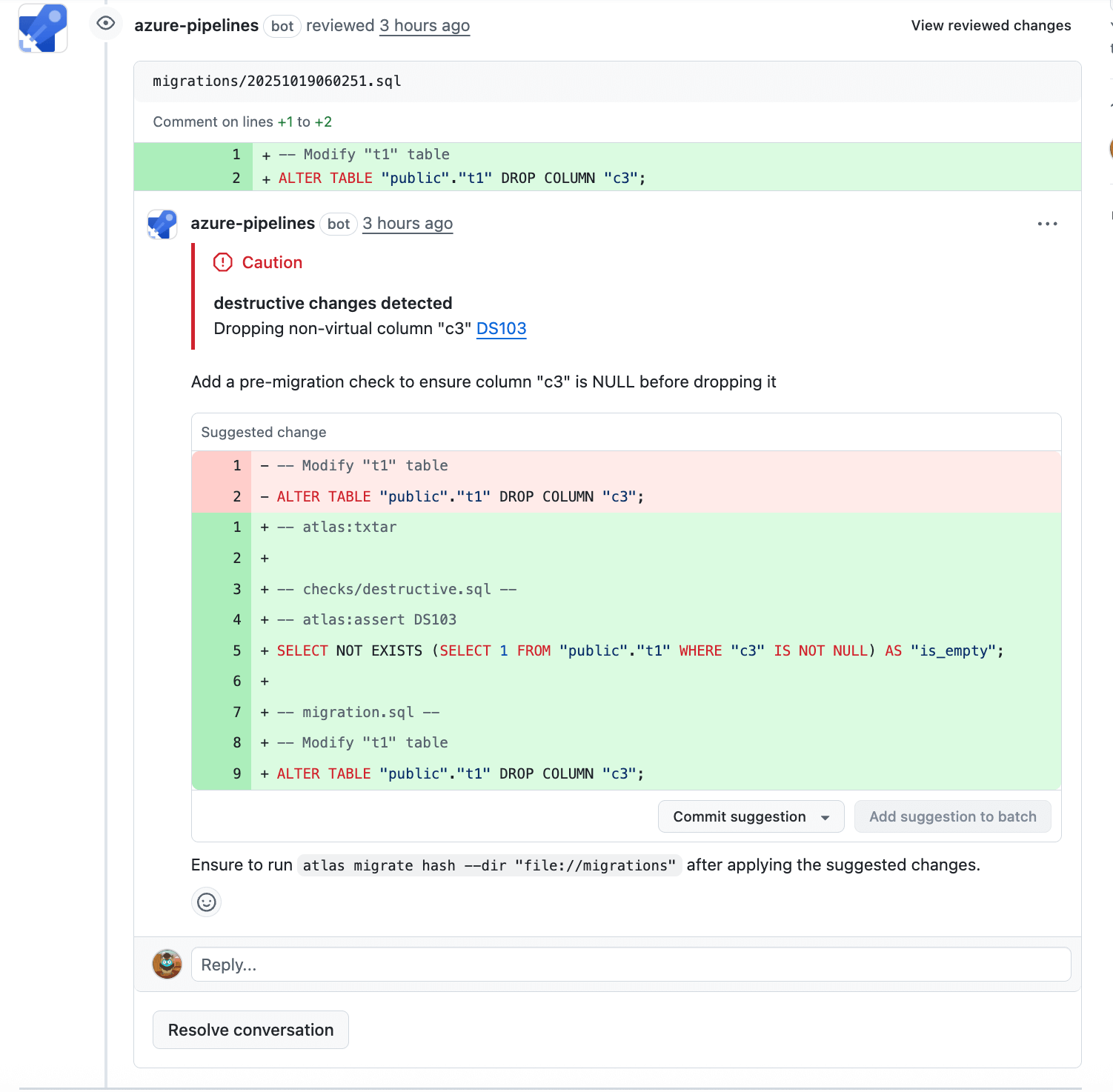
-
Check the lint report. Follow any instructions to fix the issues.
-
Merge the pull request into the main branch. This will trigger the
migrate pushandmigrate applysteps. -
When the pipeline finishes running, check your database to see if the changes were applied.