Linting Django Schemas
Linting Django Schemas with Atlas
Django is a powerful web framework that includes a built-in ORM, allowing developers to define their data models using Python classes. However, mistakes are always possible. Atlas provides a way to lint your Django schemas, ensuring that they follow best practices and are free of common issues.
atlas schema lint --env django
Getting Started with Atlas and Django
First things first, ensure you have the Atlas Django Provider installed on your Django project. To set up, follow the getting started guide.
Enforcing naming conventions
Atlas allows you to enforce naming conventions for your Django models, fields, and other schema objects. This helps maintain consistency across your codebase and makes it easier to understand.
You can define naming conventions in your Atlas configuration file (atlas.hcl), which will be used to lint your Django schemas.
lint {
naming {
match = "^[a-z]+$"
message = "must be lowercase"
}
}
Custom Linting Rules
You can also define custom linting rules for your Django project to enforce specific coding standards or best practices that are unique to your application.
- Timestamp Columns
- Function Prefixes
- Not Null Foreign Keys
predicate "column" "not_null" {
variable "name" {
type = string
}
variable "type" {
type = string
}
name {
eq = var.name
}
type {
eq = var.type
}
null {
eq = false
}
}
predicate "table" "has_timestamp_columns" {
any {
column {
predicate = predicate.column.not_null
vars = {
name = "created_at"
type = "timestamp"
}
}
}
any {
column {
predicate = predicate.column.not_null
vars = {
name = "updated_at"
type = "timestamp"
}
}
}
}
rule "schema" "table-required-columns" {
description = "All tables must include created_at and updated_at columns with NOT NULL constraints"
table {
assert {
predicate = predicate.table.has_timestamp_columns
message = "table ${self.name} must have created_at and updated_at columns"
}
}
}
predicate "function" "match_name" {
variable "pattern" {
type = string
}
name {
match = var.pattern
}
}
rule "schema" "function-naming" {
description = "Ensure all functions are lower-cased and prefixed with func_"
schema {
function {
assert {
predicate = predicate.function.match_name
vars = { pattern = "func_[a-z]+" }
message = "function ${self.name} must be lower-cased and prefixed with func_"
}
}
}
}
predicate "foreign_key" "not_nullable" {
all {
column {
condition = !self.null
}
}
}
rule "schema" "foreign-key-not-nullable" {
description = "Foreign keys must not be nullable"
table {
foreign_key {
assert {
predicate = predicate.foreign_key.not_nullable
message = "Foreign key ${self.name} must not be nullable"
}
}
}
}
Read our Custom Schema Rules guide to start writing your own custom rules.
CI/CD Integration
To ensure that your Django schemas are always linted, you can use the ariga/atlas-action/schema/lint
GitHub Action in your CI/CD pipeline. This will automatically run the atlas schema lint command on your Django models when
pushing changes to a pull request.
name: Lint Django Schema
on: [pull_request]
jobs:
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }}
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: '3.11'
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
pip install django atlas-provider-django
- name: Setup Atlas
uses: ariga/setup-atlas@v1
with:
cloud-token: ${{ secrets.ATLAS_CLOUD_TOKEN }}
- name: Setup Atlas action
uses: ariga/atlas-action/setup@v1
- name: Lint Django Schema
uses: ariga/atlas-action/schema/lint@v1
with:
env: django
dev-url: 'sqlite://?mode=memory&_fk=1'
url: 'env://url'
If there are any issues, the action will report them via a comment and warning annotations on the pull request. This helps maintain code quality and ensures that any issues are always caught before reaching production.
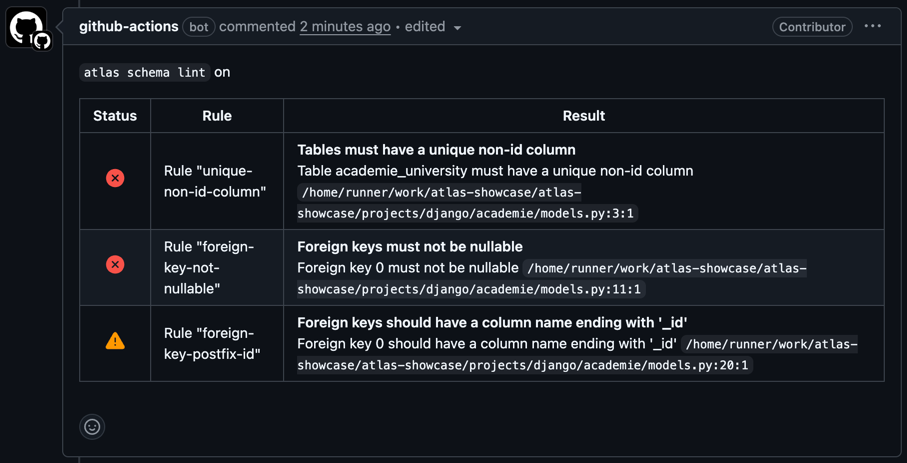
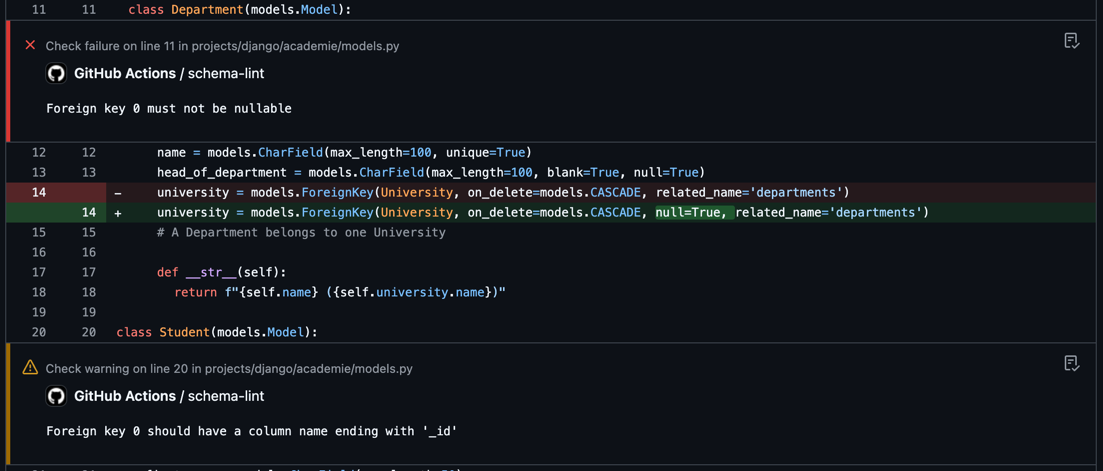
Example
Check out this project for a complete setup of linting Django schemas with Atlas.
Conclusion
Using Atlas to lint your Django schemas can help you catch potential issues early in the development process, ensuring that your application is built on a solid foundation. By integrating Atlas into your Django workflow, you can improve the quality of your code and reduce the risk of issues in production.